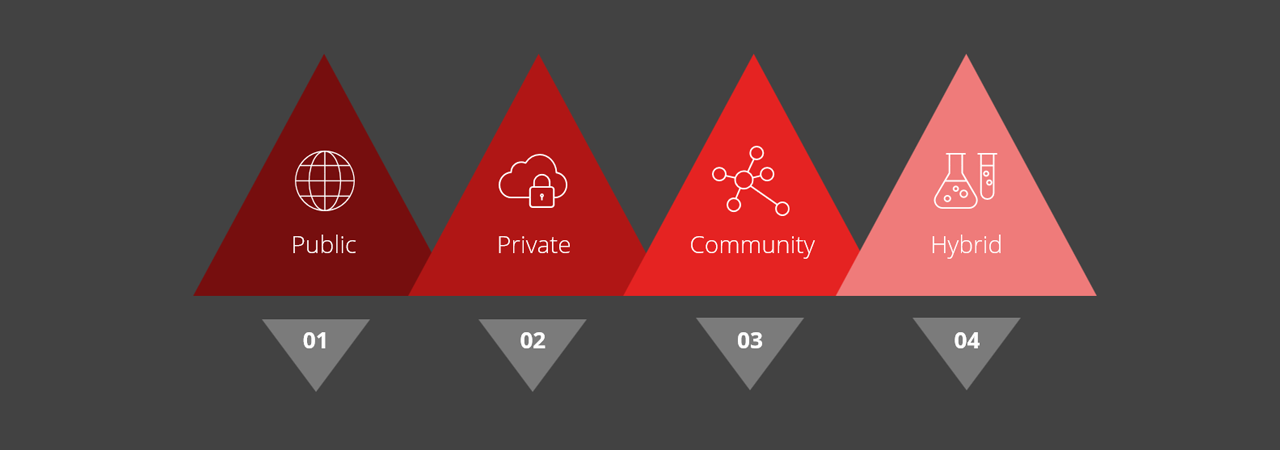
TYPES OF IOT INFRASTRUCTURE
Our customers enjoy the freedom to choose which type of IoT communication infrastructure they would like to use. Either to build their own Switzercloud IoT infrastructure by installing their own gateways or alternatively, they can use already existing networks such as public or open community-based ones.
-
Public IoT
Radio infrastructure owned and run by telecoms carriers or a 3rd-party operator. Open to the public regionally or nationwide. The operator determines which type (indoor/outdoor) and area (rural, suburban, urban) of coverage to support. Service is sold by subscription and other fees may be charged for example volume of data, number of messages, amount of devices. Examples are: Swisscom, Sigfox, etc
-
Private
A private company, joint project or consortium that builds and manages its own IoT network. The network is not offered to the public. The IoT use case and location of its users define the type and area of coverage. The network is expanded according to the plans of the business. Examples are: Utilities, cities and other businesses.
-
Open Community
Also known as Viral networks, are open-community networks aimed to provide free IoT access to everyone. Usually driven by groups of developers and enthusiasts, IoT infrastructure is built by member-donated gateways. Members contribute to providing operations support and also software development. An example is: The Things Network.
-
Hybrid
Usually a mix of Private and Community models. Hybrid models are a union of multiple private networks joined to form a large IoT network. Each new gateway extends connectivity for all members. This levers the benefit of shared IoT infrastructure, as each member at times may use a foreign gateway to transport data. An example is: The Switzercloud.
Not sure which model is best for you?
Discuss this with us at any time, obligation free. Of course, we are also happy to support you for any other questions.
Diese E-Mail-Adresse ist vor Spambots geschützt! Zur Anzeige muss JavaScript eingeschaltet sein!
Learn more
Switzercloud Solutions
LoRaWAN, Sigfox, NB-IoT, etc.
Get in touch
Back to overview
What is LoRaWAN
LoRaWAN® (LOng RAnge Wide Area Network) is a wireless and energy-efficient LPWAN (Low Power WAN) protocol suited for IoT solutions. Levering its energy-efficient properties, measured data can be read from sensors and commands can be sent to IoT devices.

-
Range
With LoRaWAN® data can be transmitted wirelessly over several kilometres and can penetrate deep into buildings and basements. Topography such as hills, buildings and other objects can have an impact on actual range. Especially with indoor applications below ground level, achievable distances are often reduced to less than 1km. However, this is still superior when compared to other existing wireless technologies.
-
Energy Requirements
IoT devices and LoRaWAN® technology itself, requires very little power during operation. Many sensors are battery-powered and work for up to 10 years or more without battery replacement. The achievable lifetime depends on the amount of data, the frequency of tansmission and the radio quality.
-
ISM Band
An ISM frequency band is license-free for use and is used in many everyday applications such as garage door controls or home baby monitors. The ISM frequency range of LoRaWAN® in Europe is around 868 MHz. In other countries, the frequencies are different, but always below 1'000 MHz.
-
Cost Structure
One-time only prices for LoRaWAN® IoT devices range between 20.- and around 350.- Swiss Francs. For very specific applications & high-quality measuring devices, prices start from around 500 CHF.
Operationally, the connection cost of a LoRaWAN ™ device is around CHF 10.- per year and hLoRaWAN® cheaper, for example, than a SIM subscription.
-
Ecosystem
More and more hardware or software manufacturers and suppliers are members of the international, non-profit organization, The LoRa® Alliance. This fast growing community of over 500 members is responsible for the further development of LoRaWAN®.
-
Ownership of LoRaWAN®
The LoRaWAN® specification, set by the LoRa® Alliance, is freely available and uses a proprietary and patented transmission method called LoRa® from Semtech Corporation.
Learn more
Switzercloud Solutions
LoRaWAN, Sigfox, NB-IoT, etc.
Get in touch
Back to overview
What is LPWAN / LPN
Radio networks transporting small IoT data over long distances are referred to as Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) or Low Power Network (LPN).
Such networks are well suited to meet the challenges of data transmission in a city, community or within a building. Sensors and actuators, usually battery operated, can transmit or receive IoT data over several years.
LoRaWAN®, Sigfox or NB-IoT are all LPWAN / LPN protocols with similar characteristics.

-
Range
Compared to other radio-based technologies, LPWAN / LPN protocols are characterized by long range data transmission. Data can be transmitted over several kilometers. Additionally, better penetration into buildings is possible than with previously available equivalent technologies - reaching several floors into a building.
-
Data Volume
When considering IoT data amounts, sensors transmit very small amounts of data.
For example, the state of a door is transmitted with a binary 1 or 0. With this very small information the state of the door being open or closed can be processed further.
Similarly a water meter has little data to transmit even if it has a reading of 6'972m3. Sensors for Level, GPS Position, Parking, Humidity, Temperature or People Counting are all in the low volume LPWAN category.
Learn more
Switzercloud Solutions
LoRaWAN, Sigfox, NB-IoT, etc.
Get in touch
Back to overview



